

"Discover why Srishty Khera & Team Study Abroad Campus is the trusted choice for MBBS Abroad - watch our student and parent testimonials today!"

European University Overview
Europe, a continent steeped in history, culture, and diversity, boasts some of the oldest and most prestigious universities in the world. From the cobblestone streets of Oxford to the bustling campuses of Berlin, European universities offer a myriad of opportunities for academic exploration and personal growth. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the rich tapestry of higher education institutions across Europe.
Diversity in Education: One of the most striking features of European universities is their diversity. Each country has its own unique approach to higher education, reflecting its cultural values and educational traditions. For example, the UK’s Oxbridge model emphasizes tutorial-based learning and independent study, while universities in countries like Germany and France often follow a more structured, lecture-based format.
Prestigious Institutions: Europe is home to some of the most prestigious universities in the world, consistently ranking high in global university rankings. Institutions like the University of Oxford, the University of Cambridge, and the Sorbonne have long been synonymous with academic excellence and intellectual rigor. These universities attract students and scholars from around the globe, fostering a vibrant international community of learners.
Multilingual Environment: One of the unique aspects of studying in Europe is the opportunity to immerse oneself in a multilingual environment. Many European universities offer courses in multiple languages, allowing students to pursue their studies in English, French, German, Spanish, and more. This linguistic diversity not only enriches the learning experience but also prepares students for an increasingly interconnected world.
Innovative Research: European universities are at the forefront of groundbreaking research and innovation across a wide range of disciplines. From cutting-edge developments in science and technology to groundbreaking discoveries in the humanities and social sciences, European researchers are pushing the boundaries of knowledge and driving positive change in society.
Student Life: Beyond academics, European universities offer a vibrant and dynamic student life experience. From student clubs and societies to cultural events and festivals, there are endless opportunities for students to engage with their peers and explore their interests outside of the classroom. Whether it’s attending a lecture by a renowned scholar or participating in a campus protest, students are encouraged to be active participants in university life.
Conclusion: In conclusion, European universities offer a rich and diverse educational experience that is unparalleled in its breadth and depth. With a legacy of academic excellence, a commitment to innovation, and a vibrant student community, Europe remains a top destination for students seeking a world-class education. Whether you’re drawn to the historic halls of Oxford or the cosmopolitan energy of Paris, there’s a European university waiting to welcome you with open arms.
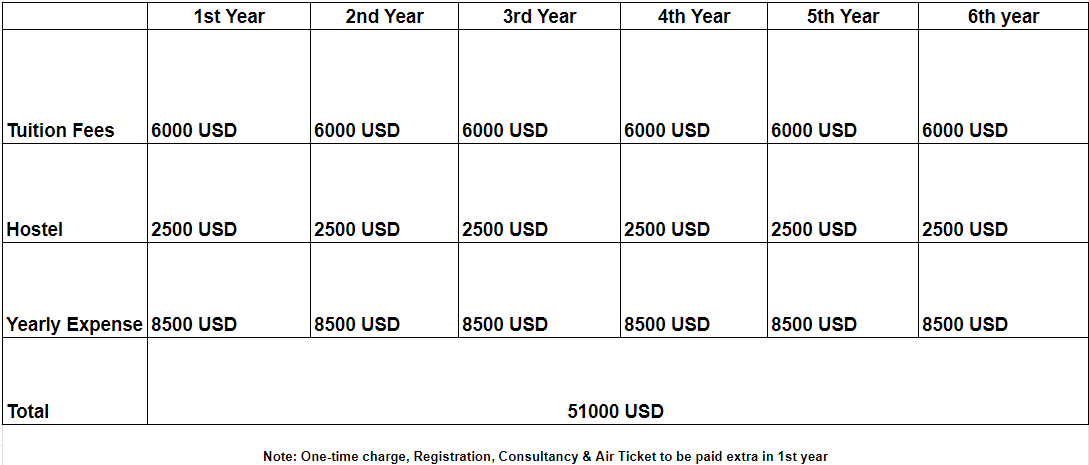
European University Fee Structure 2024-25

European University Course Duration
Embarking on a journey through higher education in Europe unveils a mosaic of educational systems, each with its own unique characteristics, including the duration of courses. Unlike the standardized course lengths prevalent in some regions, European universities offer a diverse array of program durations, reflecting the continent’s rich cultural and educational heritage. Let’s delve into the intricacies of European university course durations and unravel the threads that weave this fascinating tapestry.
Variety in Program Lengths: One of the defining features of European higher education is the variety of program lengths available to students. While bachelor’s degrees typically span three to four years in countries like the United Kingdom and France, other nations, such as Germany and the Netherlands, offer shorter undergraduate programs, often completed in three years. Conversely, some countries, like Italy and Spain, may require students to complete longer undergraduate programs, lasting up to five or six years, particularly in fields such as medicine and engineering.
Master’s programs exhibit a similar diversity, with durations ranging from one to two years across different European countries. Additionally, integrated bachelor’s and master’s programs, commonly found in countries like Germany, Switzerland, and Scandinavia, allow students to earn both degrees within a condensed timeframe, typically five years or less.
Flexible Learning Pathways: European universities prioritize flexibility and academic freedom, allowing students to tailor their educational journey to suit their interests and goals. This flexibility extends to program durations, with options for part-time study, accelerated programs, and opportunities for credit transfer and recognition of prior learning. Such flexibility enables students to design personalized learning pathways that accommodate their individual circumstances and aspirations.
Impact on International Mobility: The diversity in course durations within European universities has significant implications for international mobility and student exchange programs. Students accustomed to a specific course length in their home country may encounter varying structures and durations when studying abroad, necessitating careful planning and coordination. Nevertheless, this diversity enriches the international student experience, fostering cross-cultural understanding and adaptability.
Quality Assurance and Accreditation: Despite the differences in course durations, European higher education systems adhere to rigorous quality assurance standards to ensure academic excellence and comparability across programs. Accreditation bodies, such as the European Quality Assurance Register for Higher Education (EQAR) and national agencies, play a vital role in evaluating and monitoring the quality of education provided by universities, regardless of program length. This commitment to quality ensures that students receive a high standard of education, irrespective of the duration of their chosen program.
Conclusion: In conclusion, European university course durations reflect the continent’s cultural diversity, educational traditions, and commitment to academic excellence. From short, intensive programs to more extended, comprehensive pathways, students have the opportunity to navigate a rich tapestry of educational experiences. As students embark on their academic journey in Europe, they are invited to embrace the diversity of program lengths, knowing that each thread contributes to the vibrant fabric of European higher education.
Eligibility Criteria by European University
As students worldwide seek to embark on their academic journey, European universities stand out as beacons of opportunity, offering a diverse range of educational programs and experiences. However, gaining admission to these esteemed institutions often requires navigating a labyrinth of eligibility criteria, each university with its own set of requirements. Let’s delve into the intricacies of eligibility criteria set forth by European universities, uncovering the nuances that shape the admissions process.
Academic Excellence: At the heart of European university admissions lie considerations of academic excellence. While specific criteria may vary between institutions and programs, prospective students are typically evaluated based on their academic achievements, including grades, standardized test scores, and qualifications obtained. Universities seek candidates who demonstrate intellectual curiosity, critical thinking skills, and a passion for learning, traits indicative of success in higher education.
Language Proficiency: Given the multilingual nature of Europe, language proficiency often plays a crucial role in determining eligibility for admission. Many universities require international applicants to demonstrate proficiency in the language of instruction, whether it be English, French, German, or another language. Proficiency may be assessed through standardized tests such as the TOEFL, IELTS, or Cambridge English exams, ensuring that students possess the linguistic skills necessary to thrive in a diverse academic environment.
Subject-Specific Requirements: In addition to general academic qualifications, certain programs may have specific subject requirements tailored to the field of study. For example, STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) programs may require proficiency in mathematics and the sciences, while humanities programs may prioritize language and literature skills. Prospective students are encouraged to familiarize themselves with program-specific requirements to ensure they meet the necessary prerequisites for admission.
Personal Statement and Letters of Recommendation: European universities often value holistic assessments of applicants, considering not only academic achievements but also personal attributes and potential for contribution to the university community. Personal statements, essays, or motivational letters provide applicants with an opportunity to showcase their aspirations, experiences, and motivations for pursuing higher education. Additionally, letters of recommendation from teachers, mentors, or employers may offer insight into an applicant’s character, work ethic, and academic potential.
Diversity and Inclusivity: European universities embrace diversity and inclusivity, welcoming students from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and experiences. While academic qualifications form the foundation of eligibility criteria, universities also consider factors such as socioeconomic background, extracurricular involvement, and personal circumstances in their admissions decisions. This commitment to diversity enriches the university community and fosters a culture of openness, tolerance, and mutual respect.
Conclusion: In conclusion, eligibility criteria set forth by European universities reflect a commitment to academic excellence, diversity, and inclusivity. Prospective students are encouraged to carefully review the requirements of each institution and program, ensuring they meet the necessary qualifications for admission. As students embark on their journey to higher education in Europe, they are invited to embrace the diversity of experiences and opportunities that await, knowing that each university seeks to cultivate a community of scholars dedicated to learning, discovery, and innovation.
Facilities & Infrastructure at European University
European universities are not only bastions of academic excellence but also hubs of innovation, creativity, and cultural exchange. Central to this dynamic educational environment are the state-of-the-art facilities and infrastructure that support teaching, research, and student life. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the diverse range of facilities and infrastructure available at European universities, elevating the learning experience to new heights.
Modern Campus Facilities: European universities boast modern campus facilities designed to cater to the diverse needs of students and faculty. From cutting-edge lecture halls equipped with the latest audiovisual technology to spacious libraries housing extensive collections of books and digital resources, universities offer an inspiring environment for intellectual exploration and academic collaboration. Additionally, purpose-built laboratories, studios, and workshops provide students with hands-on learning opportunities in fields ranging from science and engineering to arts and design.
Research Centers and Innovation Hubs: At the forefront of scientific discovery and technological advancement, European universities are home to world-class research centers and innovation hubs. These facilities foster interdisciplinary collaboration and serve as incubators for groundbreaking research projects and startups. From biotechnology and renewable energy to artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, research centers at European universities tackle some of the most pressing challenges facing society today, driving innovation and economic growth.
Sports and Recreation Facilities: Recognizing the importance of holistic development, European universities offer a wide range of sports and recreation facilities to promote physical well-being and healthy lifestyles among students. Campuses feature modern sports complexes, fitness centers, and outdoor recreational spaces where students can engage in various sports, fitness classes, and leisure activities. Whether it’s playing football on the campus field, swimming laps in the university pool, or participating in yoga sessions, students have ample opportunities to stay active and unwind outside of their academic pursuits.
Student Support Services: European universities prioritize the well-being and success of their students, offering a comprehensive range of support services to address their academic, personal, and social needs. Dedicated counseling centers provide confidential support for students facing academic challenges, mental health issues, or personal crises. Career services offices offer guidance on internships, job placements, and career development, helping students navigate the transition from university to the workforce. Additionally, international student offices facilitate the integration of international students into the university community, offering assistance with visa matters, accommodation, and cultural adaptation.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Initiatives: In line with global efforts to promote sustainability and environmental stewardship, European universities are implementing eco-friendly initiatives and green campus practices. Many universities have adopted sustainable building design principles, incorporating energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy sources, and eco-friendly materials into campus infrastructure. Recycling programs, waste reduction initiatives, and green transportation options further contribute to environmental conservation efforts, fostering a culture of sustainability among students and staff.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the facilities and infrastructure at European universities form the foundation of a vibrant and inclusive learning environment, fostering academic excellence, innovation, and personal growth. From state-of-the-art campus facilities to world-class research centers and student support services, universities offer a rich array of resources to support students throughout their academic journey. As students embark on their educational endeavors in Europe, they are welcomed into a community dedicated to nurturing their talents, ambitions, and aspirations, shaping the leaders and innovators of tomorrow.
Documents Required for Admission at European University
For students aspiring to pursue higher education in Europe, the journey begins with the meticulous preparation of application materials. European universities, renowned for their academic excellence and cultural diversity, require prospective students to submit a comprehensive set of documents as part of the admissions process. Let’s unravel the essential documents required for admission at European universities, guiding applicants through the intricacies of the application journey.
Academic Transcripts and Certificates: At the core of any university application are academic transcripts and certificates, providing a record of a student’s educational achievements. Prospective students must submit transcripts detailing their academic performance throughout high school or undergraduate studies, including grades, course titles, and credit hours. Additionally, universities may require certified copies of academic certificates or diplomas obtained, verifying the completion of previous qualifications.
Standardized Test Scores: Many European universities, particularly those offering programs in English, require applicants to submit standardized test scores as part of their application. Tests such as the TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language), IELTS (International English Language Testing System), or Cambridge English exams assess applicants’ proficiency in the English language. Additionally, some programs may require subject-specific standardized tests, such as the SAT (Scholastic Assessment Test) or ACT (American College Testing), particularly for undergraduate admissions.
Personal Statement or Motivational Letter: A compelling personal statement or motivational letter is a vital component of the application package, allowing prospective students to articulate their aspirations, academic interests, and reasons for choosing a particular program or university. This document provides applicants with an opportunity to showcase their personality, achievements, and suitability for the academic program, demonstrating their passion for learning and potential for success.
Letters of Recommendation: Letters of recommendation from teachers, professors, or mentors play a significant role in supporting an applicant’s candidacy for admission. These letters offer insights into an applicant’s academic abilities, character, work ethic, and potential for contribution to the university community. Recommenders should ideally be individuals who can attest to the applicant’s academic or professional qualifications and provide meaningful insights into their abilities and potential.
Passport and Identification Documents: International students applying to European universities must provide valid passport and identification documents as part of the application process. These documents verify the applicant’s identity and nationality, ensuring compliance with immigration and visa requirements. Additionally, applicants may be required to submit passport-sized photographs for identification purposes.
Proof of Financial Resources: Some European universities may request proof of financial resources to ensure that prospective students have the means to finance their studies and cover living expenses during their time abroad. This may include bank statements, sponsorship letters, or scholarship award letters demonstrating the availability of funds to support the applicant’s education and livelihood.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the documents required for admission at European universities form the cornerstone of the application process, providing universities with essential information to assess applicants’ qualifications and suitability for admission. Prospective students are encouraged to carefully review the specific requirements of each university and program, ensuring they compile a comprehensive and well-prepared application package. As students embark on their journey to higher education in Europe, meticulous attention to detail and thorough preparation will pave the way for success in the competitive admissions landscape.
European University Ranking 2024-25
The pursuit of higher education in Europe is synonymous with excellence, innovation, and academic distinction. Each year, students and scholars eagerly anticipate the release of university rankings, which serve as a compass for navigating the diverse landscape of European higher education. As we delve into the European University Ranking for the academic year 2024-25, we uncover the institutions that stand at the pinnacle of academic achievement and excellence.
Methodology: The European University Ranking 2024-25 is a testament to the meticulous methodology and rigorous evaluation criteria employed by ranking organizations. Drawing upon a comprehensive set of indicators, including academic reputation, research output, faculty quality, internationalization, and student satisfaction, ranking compilers meticulously assess the performance of universities across Europe. Additionally, considerations such as employer reputation, alumni outcomes, and industry collaborations contribute to the holistic evaluation of institutional excellence.
Top Performers: At the forefront of the European University Ranking 2024-25 are institutions renowned for their unwavering commitment to academic excellence and innovation. Universities such as the University of Oxford, the University of Cambridge, and ETH Zurich consistently occupy top positions, celebrated for their world-class research output, renowned faculty members, and vibrant academic communities. These institutions serve as beacons of inspiration and aspiration, setting the standard for academic excellence in Europe and beyond.
Emerging Trends: The European University Ranking 2024-25 also sheds light on emerging trends and patterns shaping the higher education landscape. As universities increasingly prioritize interdisciplinary collaboration, innovation, and societal impact, institutions with strengths in areas such as sustainability, digital transformation, and health sciences are gaining prominence. Moreover, the ranking highlights the growing importance of internationalization and diversity, with universities fostering cross-border partnerships, exchange programs, and multicultural learning environments.
Regional Diversity: Beyond the top performers, the European University Ranking 2024-25 celebrates the rich diversity of institutions across the continent. From historic universities nestled in medieval towns to modern campuses in bustling urban centers, Europe offers a tapestry of educational experiences and opportunities. Institutions in diverse regions, including Scandinavia, Eastern Europe, and the Mediterranean, contribute to the vibrant mosaic of European higher education, each bringing its unique strengths and contributions to the academic community.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the European University Ranking 2024-25 serves as a testament to the unwavering pursuit of excellence and innovation within European higher education. As students and scholars navigate the dynamic landscape of university rankings, they are invited to explore the diverse array of institutions shaping the future of academia and research in Europe. Whether pursuing studies in the humanities, sciences, engineering, or beyond, the ranking offers valuable insights and guidance for those embarking on their academic journey in Europe.
Hostel Facility at European University
As students embark on their educational journey in Europe, the quest for suitable accommodation is often as paramount as the pursuit of academic excellence. European universities recognize the pivotal role that hostel facilities play in shaping the student experience, offering much more than mere lodging. Let’s explore the essence of hostel facilities at European universities and the integral role they play in fostering community, convenience, and personal growth.
Community and Camaraderie: Hostel facilities at European universities serve as vibrant hubs of community and camaraderie, bringing together students from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and disciplines. Within the walls of shared dormitories and communal spaces, lifelong friendships are forged, cultural exchanges abound, and a sense of belonging flourishes. Whether through late-night study sessions, impromptu gatherings, or international potluck dinners, hostel life fosters a spirit of collaboration, mutual support, and friendship that transcends boundaries.
Convenience and Accessibility: European universities prioritize convenience and accessibility in their hostel facilities, ensuring that students have access to essential amenities and services within close proximity to their academic institutions. Hostels are strategically located on or near campus, offering easy access to lecture halls, libraries, and recreational facilities. Additionally, amenities such as dining halls, laundry facilities, and study lounges are readily available, enhancing the convenience and comfort of student living.
Cultural Exchange and Diversity: Hostel facilities serve as melting pots of cultural exchange and diversity, providing students with opportunities to learn from each other’s perspectives, traditions, and experiences. International students, in particular, find hostels to be welcoming spaces where they can immerse themselves in the local culture, practice language skills, and build cross-cultural friendships. Through multicultural events, language exchange programs, and cultural celebrations, hostels foster an inclusive and enriching environment that celebrates diversity and promotes global citizenship.
Support and Well-being: European universities recognize the importance of supporting students’ holistic well-being within hostel facilities, offering a range of support services and resources to address their physical, mental, and emotional needs. Resident advisors, trained staff members, and peer mentors provide guidance, assistance, and a listening ear to students navigating the challenges of university life. Additionally, wellness programs, counseling services, and recreational activities promote students’ physical and mental health, fostering a supportive and nurturing environment within hostels.
Personal Growth and Independence: Living in hostel facilities at European universities offers students invaluable opportunities for personal growth, self-discovery, and independence. Away from the comforts of home, students learn essential life skills such as time management, budgeting, and conflict resolution, preparing them for the responsibilities of adulthood. Moreover, the autonomy afforded by hostel living encourages students to explore their interests, pursue passions, and take ownership of their educational journey, empowering them to become self-reliant and resilient individuals.
Conclusion: In conclusion, hostel facilities at European universities embody the essence of community, convenience, and personal growth, enriching the student experience in profound ways. As students embark on their educational journey in Europe, the hostel becomes more than just a place of residence—it becomes a home away from home, a sanctuary of friendship and support, and a crucible of personal transformation. Through shared experiences, cultural exchange, and lifelong memories, hostel living fosters connections that endure long after graduation, shaping the fabric of student life in Europe for generations to come.
Admission Process for European University
Embarking on the journey of higher education in Europe is a dream for many students worldwide, drawn by the continent’s rich history, cultural diversity, and renowned academic institutions. However, gaining admission to European universities requires navigating a comprehensive and sometimes intricate admission process. Let’s unravel the steps and intricacies of the admission process for European universities, guiding aspiring students towards their academic aspirations.
Research and Selection: The first step in the admission process for European universities is thorough research and careful selection of potential institutions and programs. Students should consider factors such as academic reputation, program offerings, faculty expertise, location, and cultural fit when compiling a list of prospective universities. Online resources, university websites, and consultation with academic advisors can provide valuable insights to aid in the decision-making process.
Application Preparation: Once prospective universities have been identified, students must meticulously prepare their application materials. This typically includes academic transcripts, standardized test scores (such as the SAT or ACT for undergraduate admissions, or the GRE or GMAT for graduate admissions), letters of recommendation, a personal statement or essay, and proof of language proficiency for non-native speakers of the language of instruction.
Language Proficiency: Proficiency in the language of instruction is a crucial requirement for admission to European universities, particularly for programs taught in languages other than the student’s native tongue. Many universities accept standardized language proficiency tests such as the TOEFL, IELTS, or Cambridge English exams as evidence of language proficiency. Some institutions may also offer language preparatory courses or require students to demonstrate proficiency through interviews or additional assessments.
Submission of Application: Once application materials are prepared, students must submit their applications by the specified deadline. Deadlines vary among universities and programs, so it’s essential to carefully review each institution’s application timeline and adhere to the submission deadlines. Online application portals or submission via postal mail are common methods for submitting applications, depending on the university’s requirements.
Evaluation and Admission Decision: After the submission of applications, universities undertake a thorough evaluation process to assess applicants’ qualifications, achievements, and suitability for admission. Admissions committees review academic transcripts, test scores, letters of recommendation, personal statements, and other supporting documents to determine each applicant’s academic potential and fit with the university’s academic community. Admission decisions are typically communicated to applicants within a specified timeframe, often through email or an online portal.
Visa and Immigration: For international students admitted to European universities, obtaining a student visa and fulfilling immigration requirements is a critical step in the admission process. Once admitted, students must follow the visa application process outlined by the respective country’s embassy or consulate. This may include providing proof of admission, financial support, health insurance, and other necessary documentation to obtain a student visa and authorization to study in the country.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the admission process for European universities is a multifaceted journey that requires careful planning, preparation, and attention to detail. By conducting thorough research, preparing application materials diligently, and adhering to deadlines, aspiring students can navigate the complexities of the admission process with confidence and clarity. As they embark on their academic journey in Europe, students are poised to embrace the rich cultural, intellectual, and personal experiences that await within the esteemed halls of European higher education.
European University Photos



European University MBBS Syllabus
Embarking on the journey to become a medical professional is a noble endeavor that requires dedication, perseverance, and a comprehensive understanding of the human body and its complexities. European universities offering MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) programs stand as pillars of medical education, providing students with a rigorous curriculum that prepares them for the challenges and responsibilities of the medical profession. Let’s delve into the intricacies of the MBBS syllabus at European universities, unraveling the path to medical excellence.
Foundational Sciences: At the core of the MBBS syllabus are the foundational sciences that form the basis of medical knowledge and practice. Students delve into subjects such as anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, gaining a deep understanding of the structure and function of the human body at the molecular, cellular, and organ system levels. Through lectures, laboratory sessions, and dissection classes, students acquire essential knowledge of human anatomy, physiological processes, biochemical pathways, and pharmacological principles, laying the groundwork for clinical practice and research.
Clinical Medicine: The MBBS curriculum at European universities seamlessly integrates clinical medicine with the foundational sciences, providing students with hands-on experience and exposure to patient care from the early years of their education. Clinical rotations in various medical specialties, including internal medicine, surgery, pediatrics, obstetrics and gynecology, psychiatry, and emergency medicine, allow students to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world clinical settings under the guidance of experienced physicians and healthcare professionals. Through bedside teaching, case discussions, and practical training, students develop clinical skills, diagnostic acumen, and patient management abilities essential for competent medical practice.
Medical Ethics and Professionalism: In addition to scientific and clinical education, European MBBS programs emphasize the importance of medical ethics, professionalism, and compassionate care. Students explore ethical principles, legal regulations, and professional standards governing the practice of medicine, learning to navigate complex ethical dilemmas and uphold the highest standards of integrity, honesty, and empathy in their interactions with patients, colleagues, and the broader community. Through reflective practice, role-playing scenarios, and discussions on ethical issues in healthcare, students cultivate the values and attitudes necessary for ethical and responsible medical practice.
Research and Innovation: European MBBS programs foster a culture of research and innovation, encouraging students to engage in scholarly activities and contribute to advancements in medical science and clinical practice. Research methodology courses, elective research projects, and opportunities for clinical research enable students to develop critical thinking skills, research competencies, and a spirit of inquiry that prepares them to be lifelong learners and leaders in their respective fields. By participating in research endeavors, students contribute to the collective knowledge base of medicine and drive positive change in healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the MBBS syllabus at European universities represents a holistic and comprehensive approach to medical education, blending scientific rigor, clinical experience, ethical principles, and research innovation. Through a balanced curriculum that integrates foundational sciences, clinical medicine, medical ethics, and research endeavors, European MBBS programs prepare students to embark on fulfilling careers as competent, compassionate, and ethical healthcare professionals. As students embark on their educational journey in pursuit of medical excellence, they are equipped with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to make a meaningful difference in the lives of patients and communities around the world.
Important FAQs
Ans: European universities offer programs in various languages, with English being the most commonly used for international programs. However, language requirements vary depending on the institution and program. Many universities require proof of proficiency in the language of instruction, typically demonstrated through standardized tests such as the TOEFL or IELTS for English-taught programs.
Ans: The application process for European universities varies depending on the institution and program. Generally, prospective students are required to submit an application form, academic transcripts, standardized test scores, letters of recommendation, a personal statement or essay, and proof of language proficiency if applicable. Deadlines and application procedures may differ, so it’s essential to review each university’s requirements carefully.
Ans: Yes, many European universities offer scholarships, grants, and financial aid opportunities for international students. These scholarships may be merit-based, need-based, or awarded for specific fields of study. Additionally, governments, foundations, and external organizations may offer scholarships to support international students’ educational endeavors. Prospective students are encouraged to research scholarship opportunities and eligibility criteria through university websites and external scholarship databases.
Ans: Student life in Europe is vibrant, diverse, and enriching, offering a wealth of opportunities for cultural immersion, social activities, and personal growth. European universities typically have active student societies, clubs, and organizations catering to a wide range of interests, from sports and arts to academic and cultural pursuits. Additionally, cities across Europe boast a rich cultural heritage, vibrant nightlife, and diverse culinary scene, providing ample opportunities for exploration and adventure outside of academia.
Ans: Yes, many European countries allow international students to work part-time during their studies to supplement their income and gain valuable work experience. However, regulations regarding work permits, hours of employment, and eligibility vary by country, so it’s essential to familiarize oneself with the specific regulations of the host country. Additionally, some universities offer on-campus employment opportunities or internships as part of their programs.

